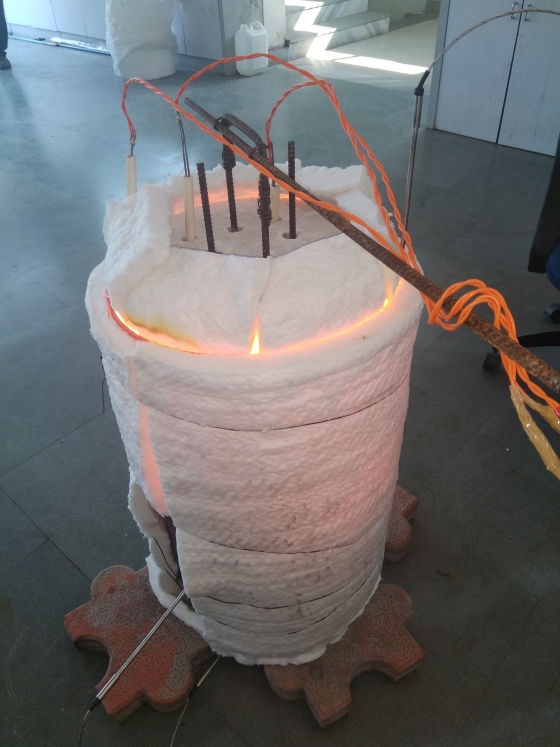
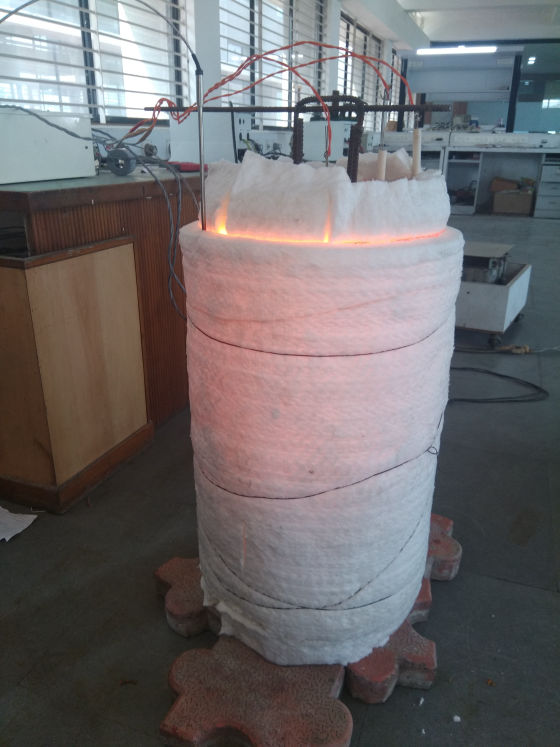
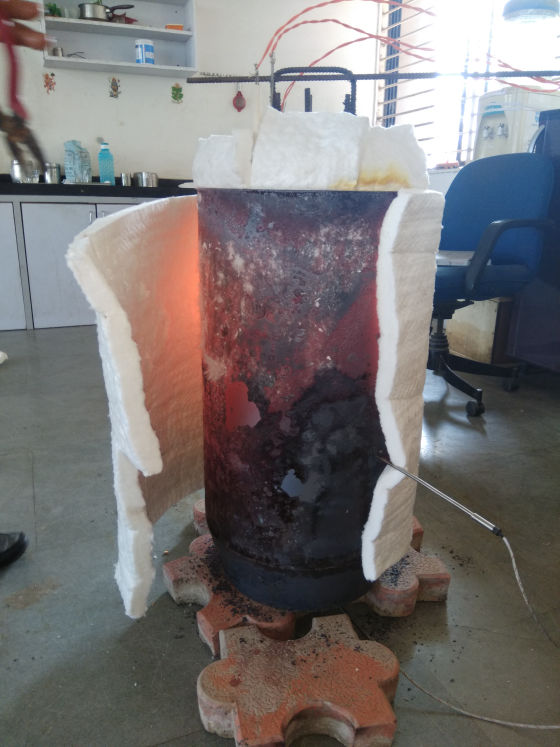
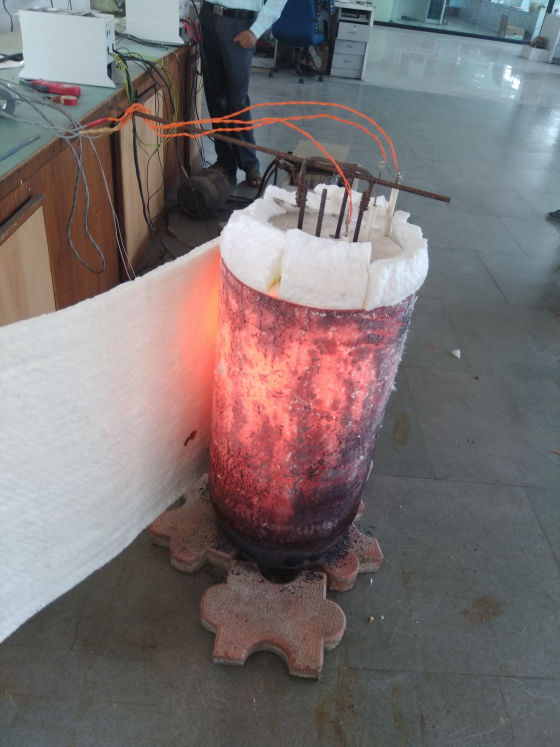
Less Energy Consumption
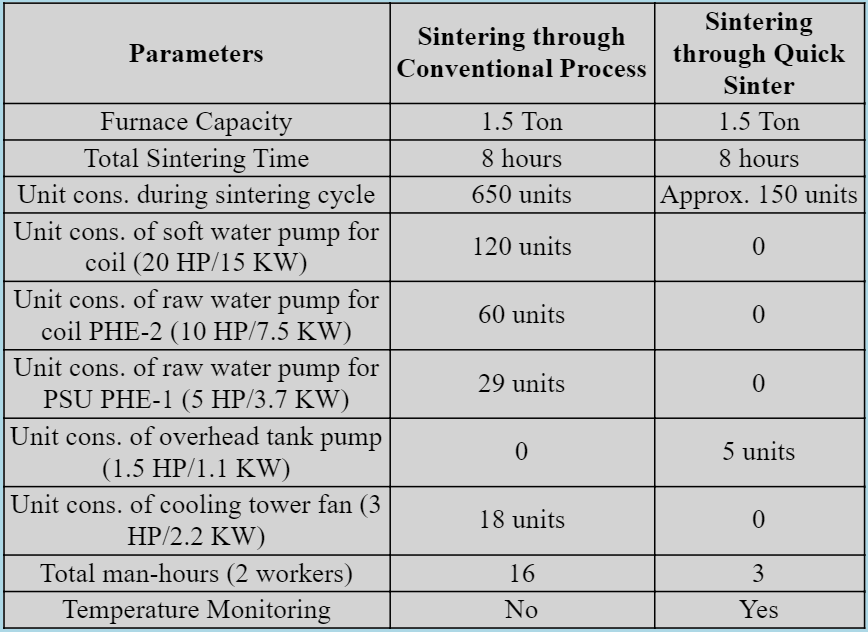
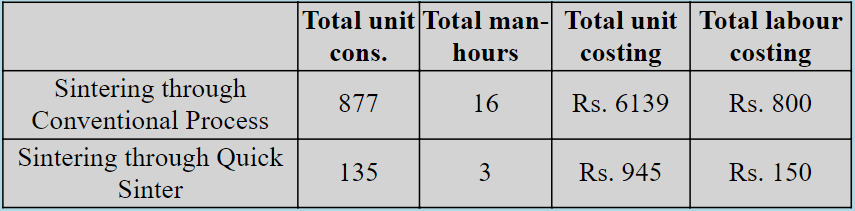
Reduced electrical costs as Quick Sinter consume at least 70-80% less unit as compared to regular Sintering heat.
More Production Output
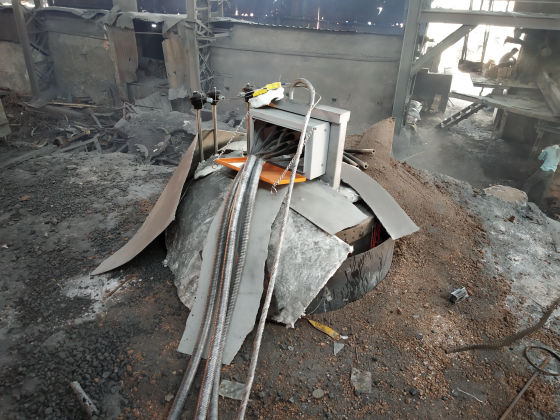
As independent power supply is used, full power of the induction PSU can be given to the other furnace during the sintering process. Thus, production is neither stopped nor slowed down.
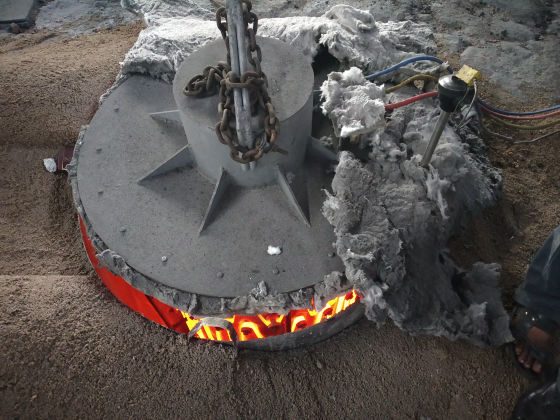
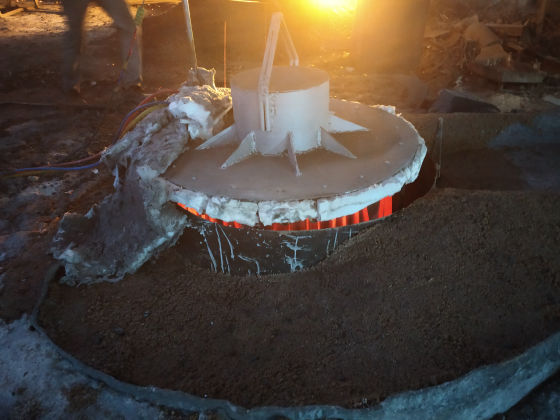
Uniform Sintering
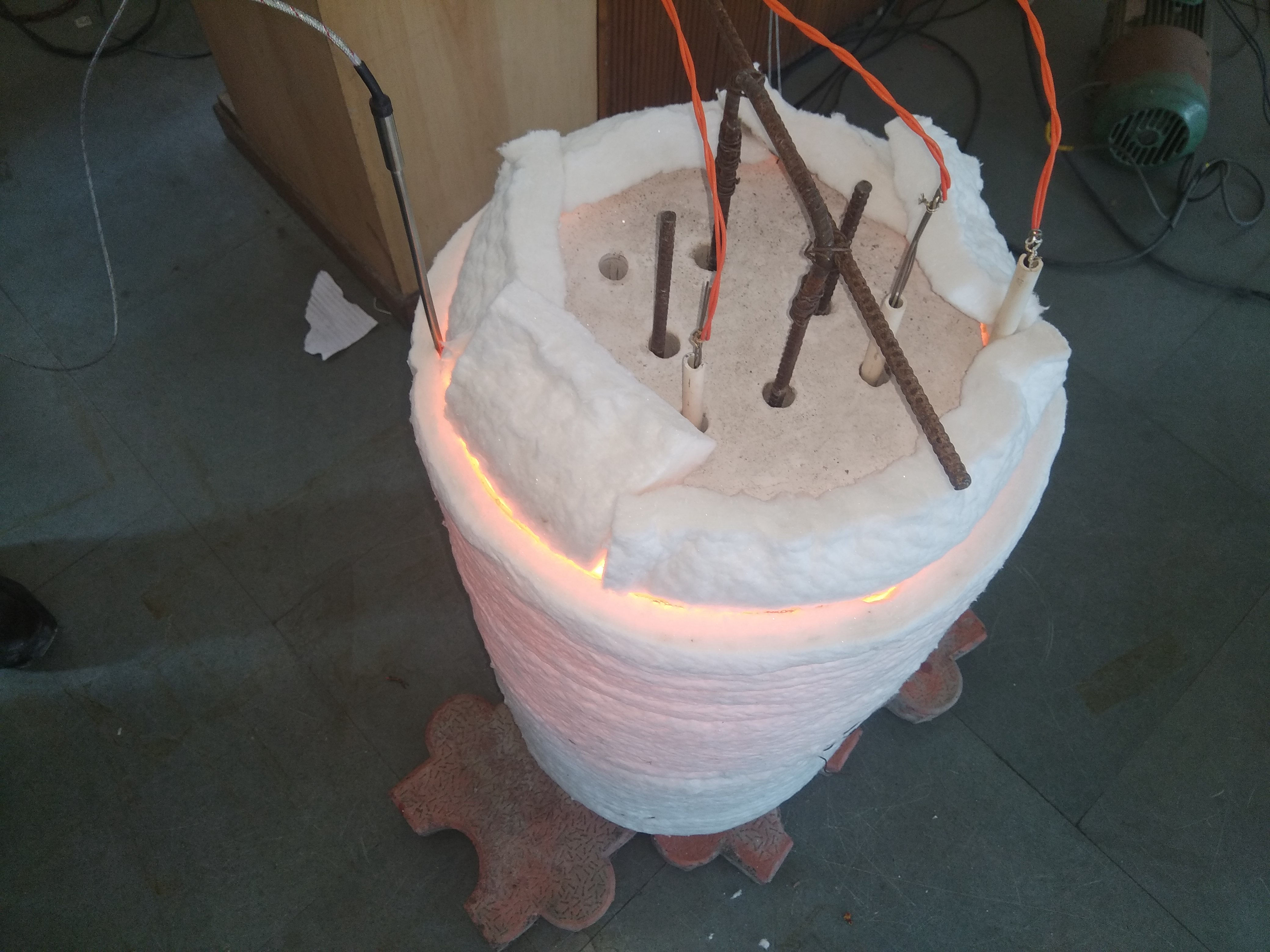
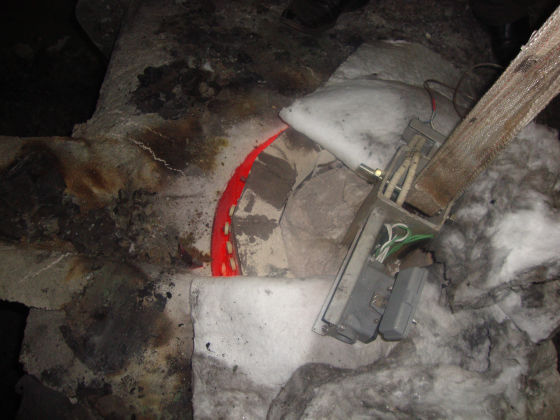
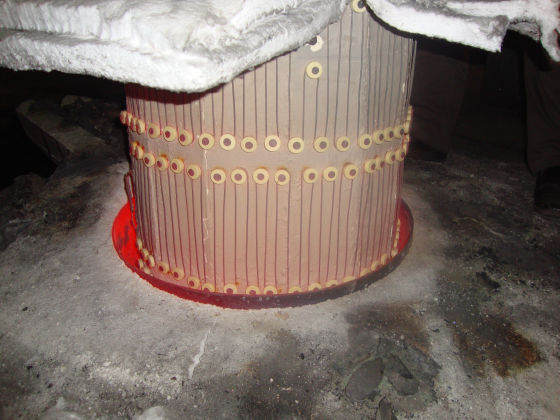
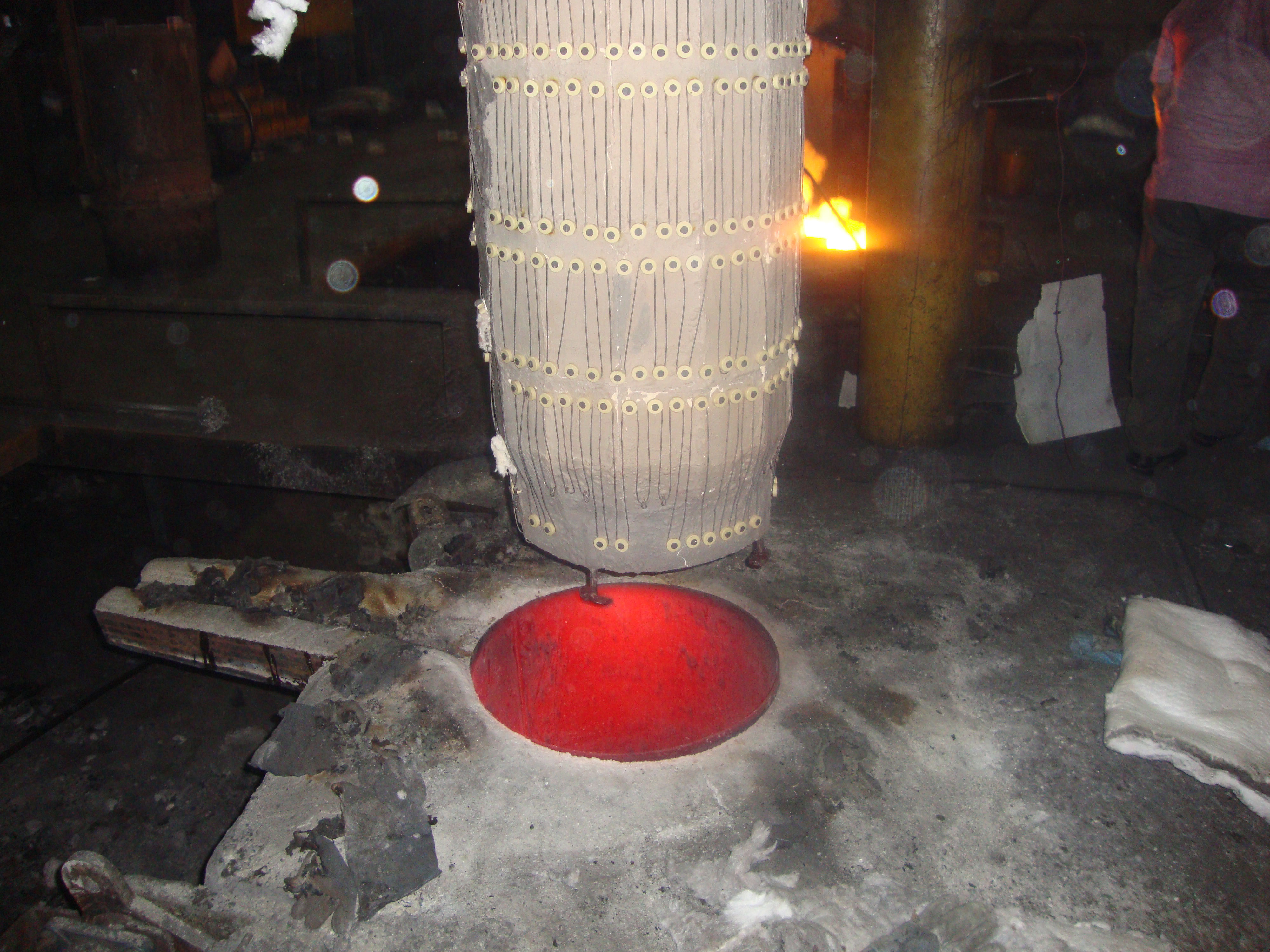
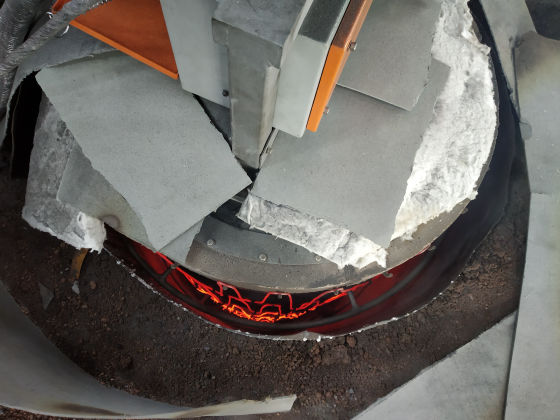
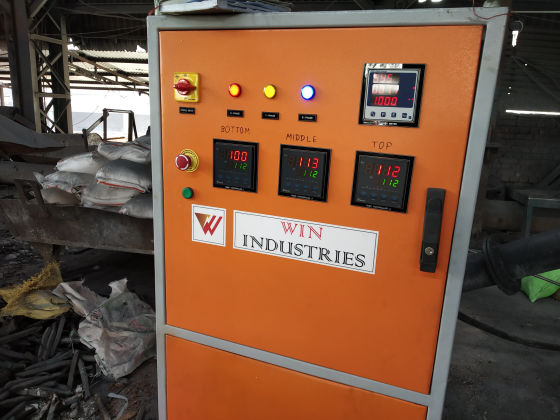
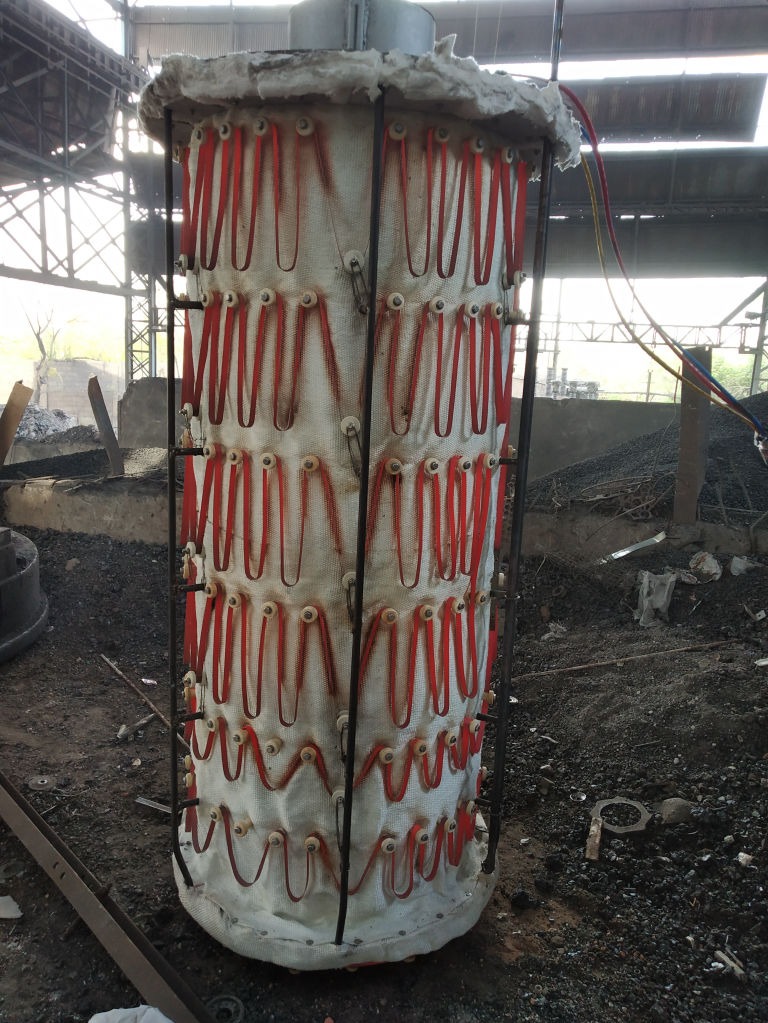
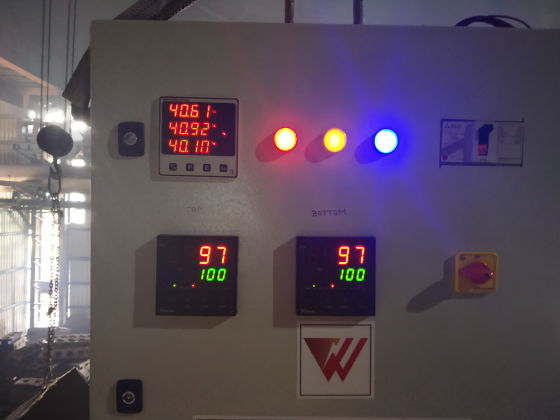
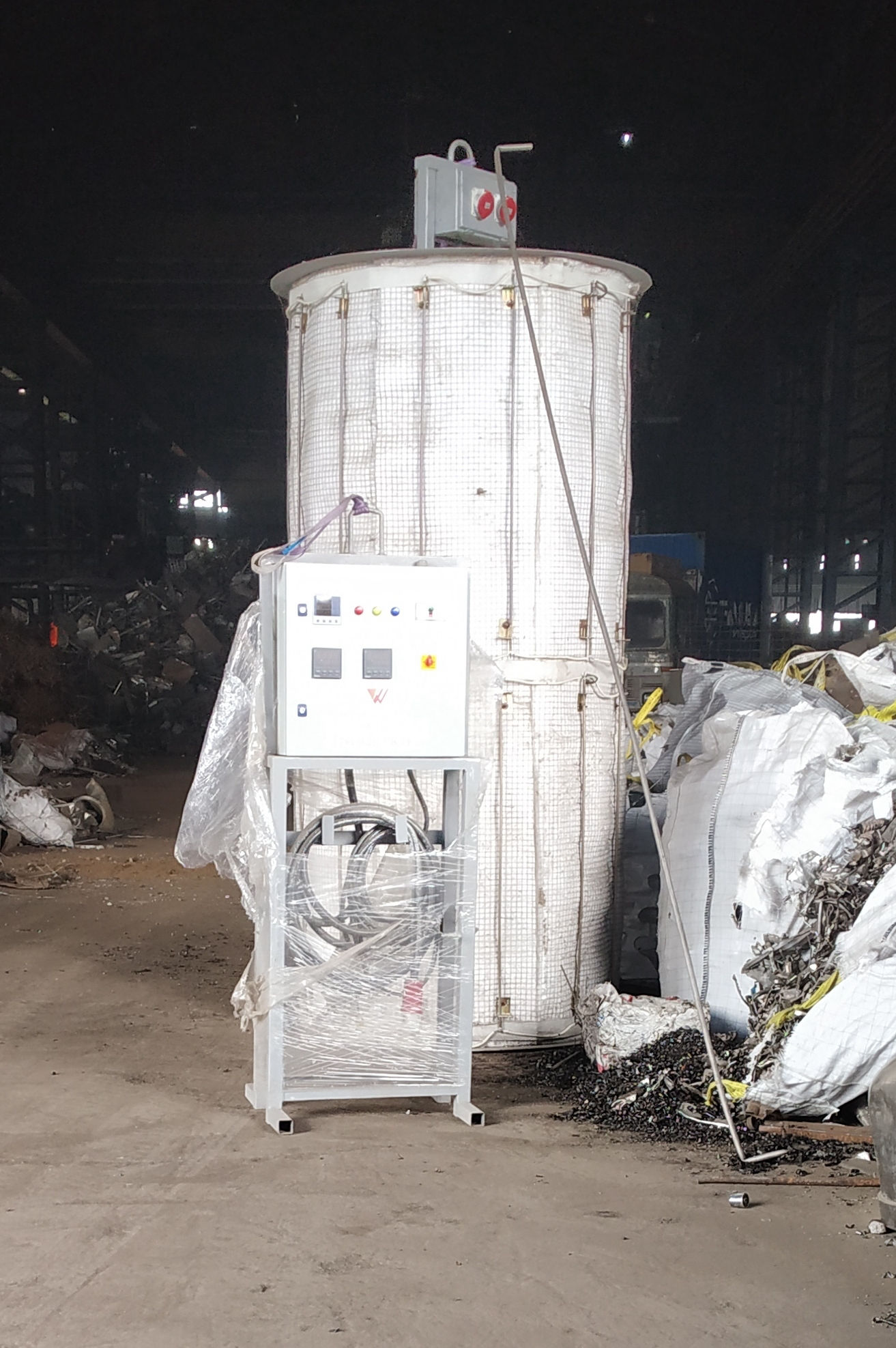
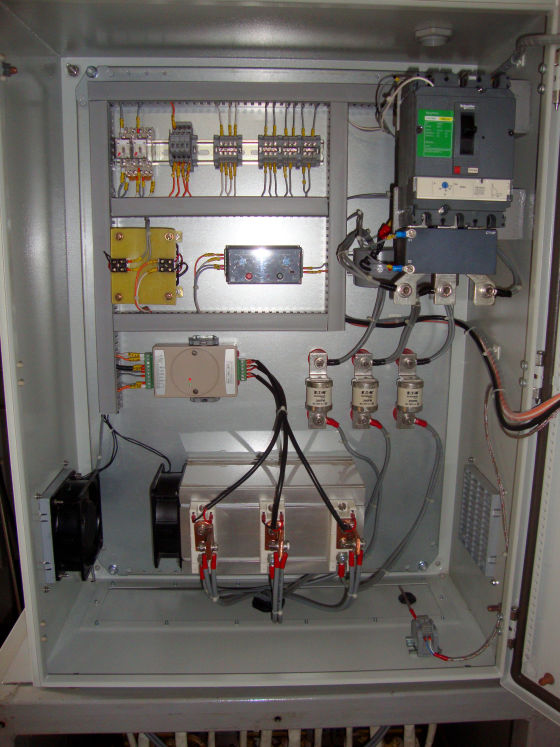
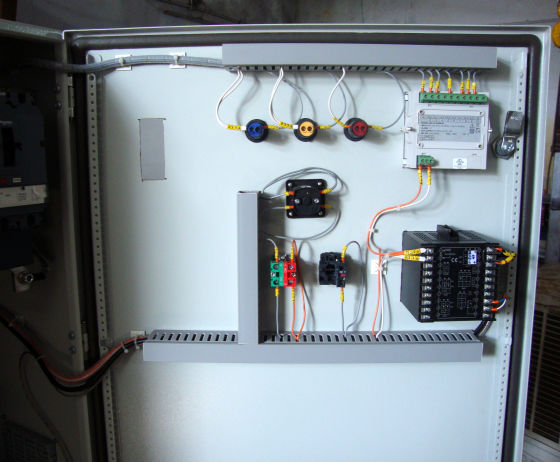
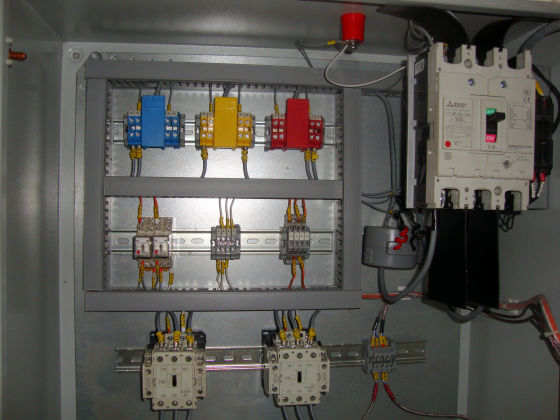
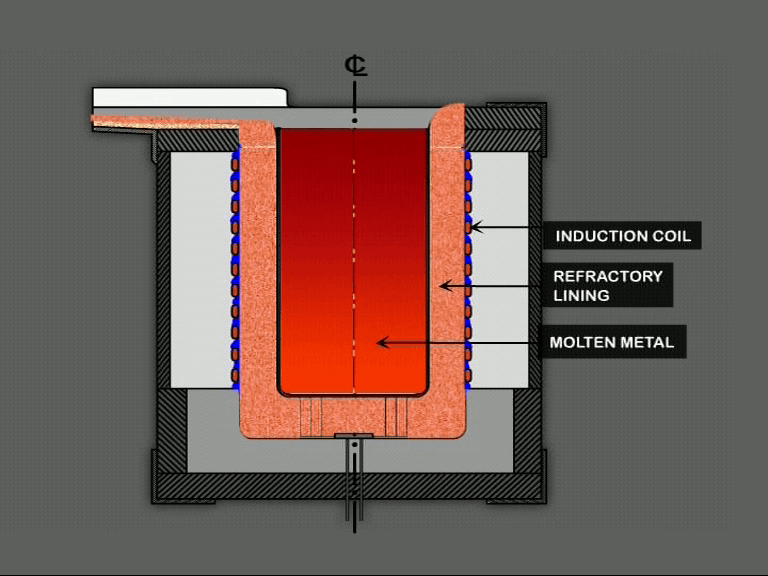
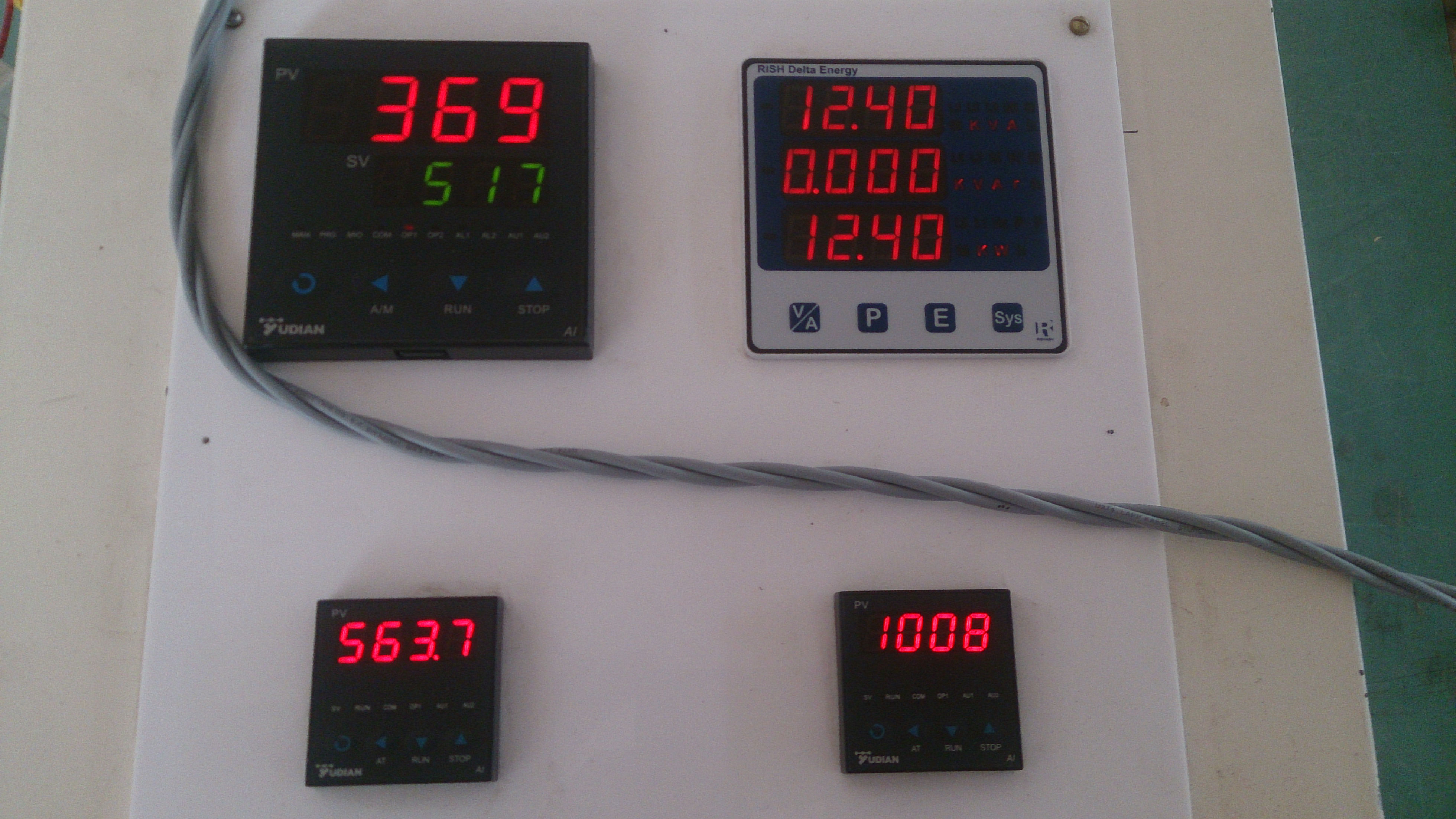
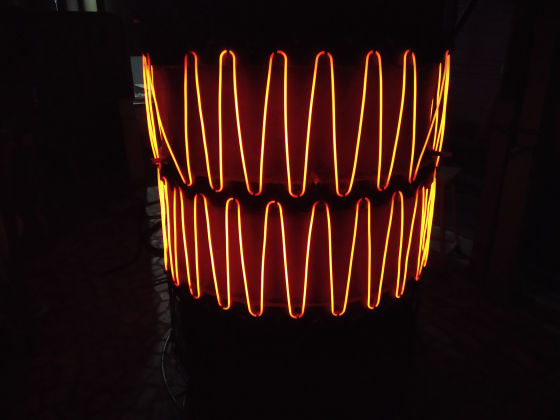
The heater is divided into 1/2/3 zones as per the furnace size and are independent of each other, giving uniform temperature from top to bottom. This ensures uniform sintering throughout the furnace.
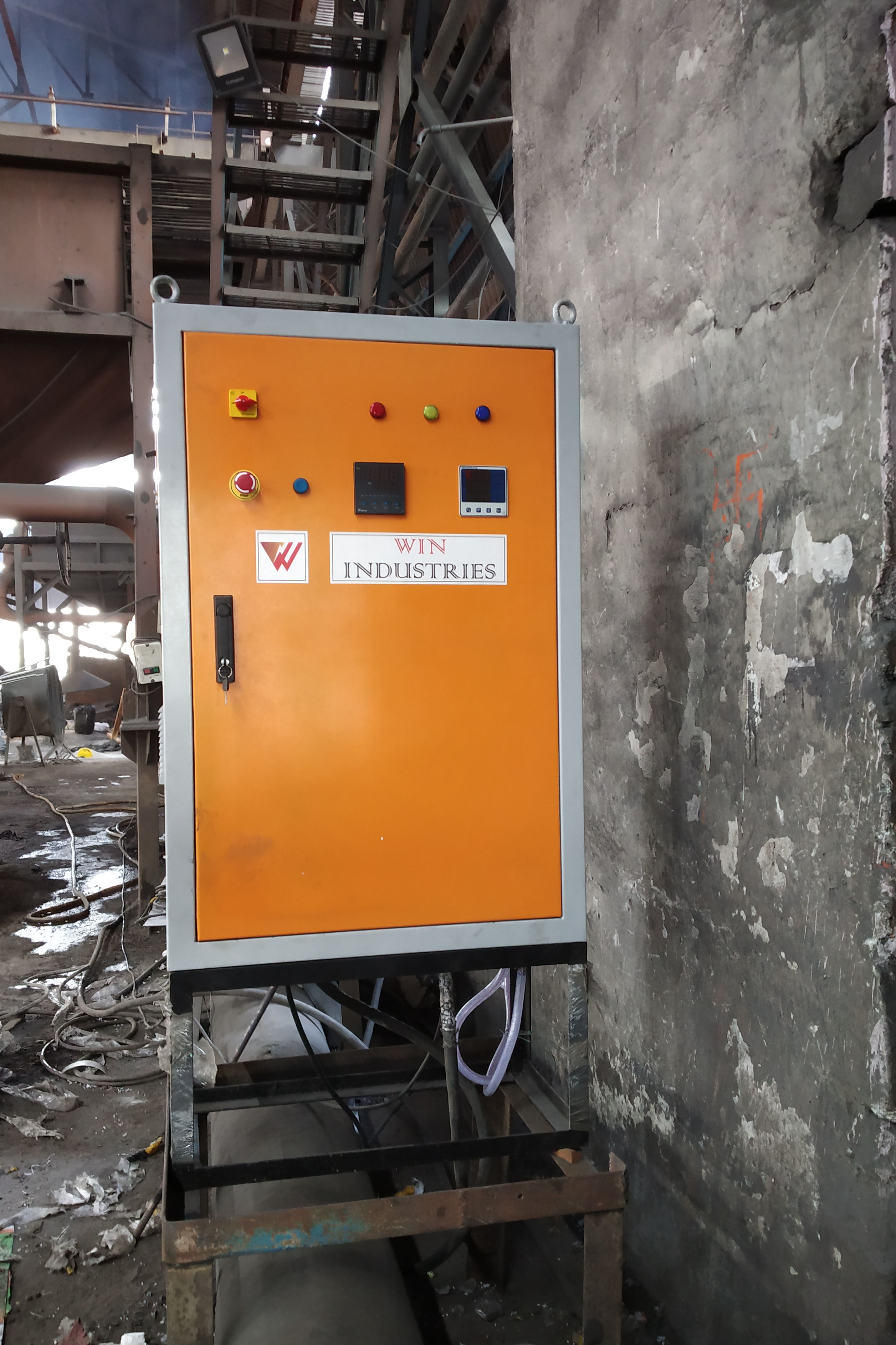
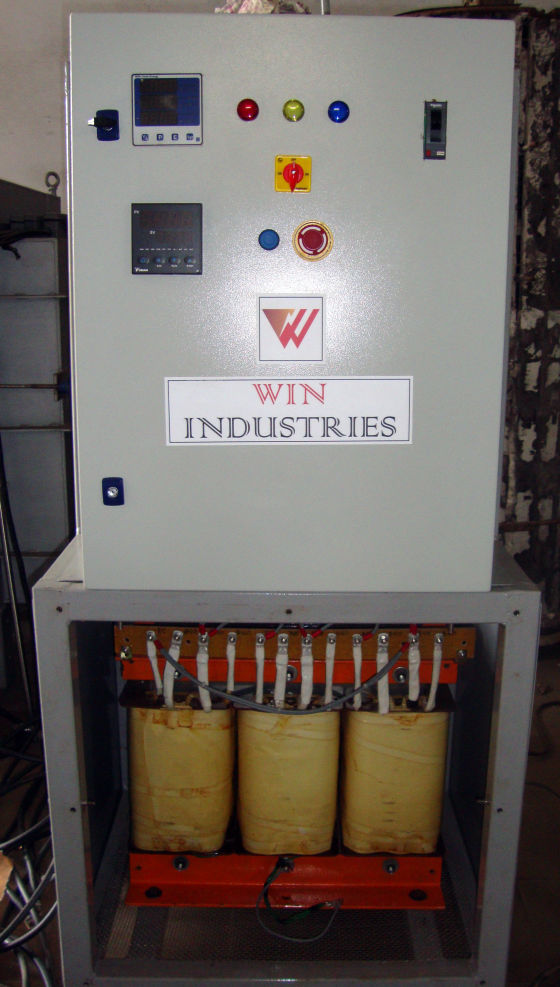
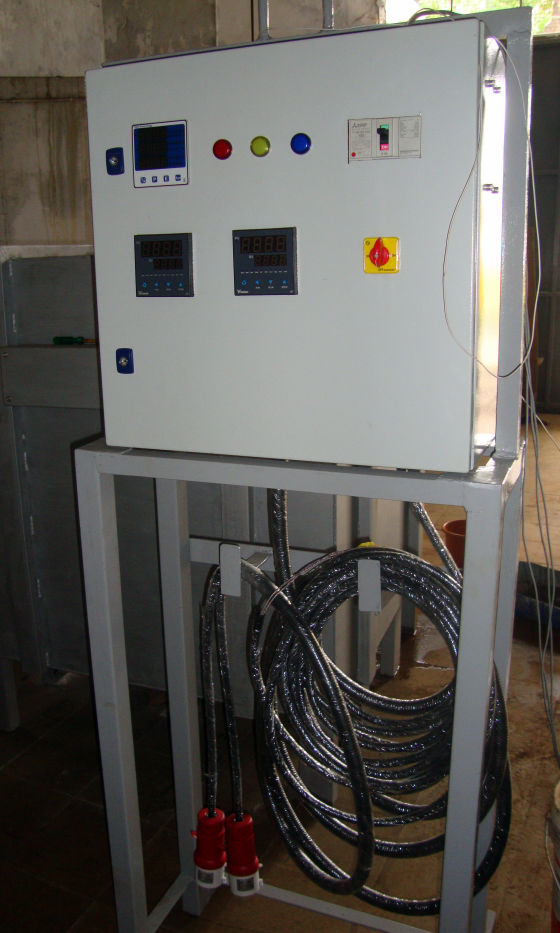
Fully Automatic
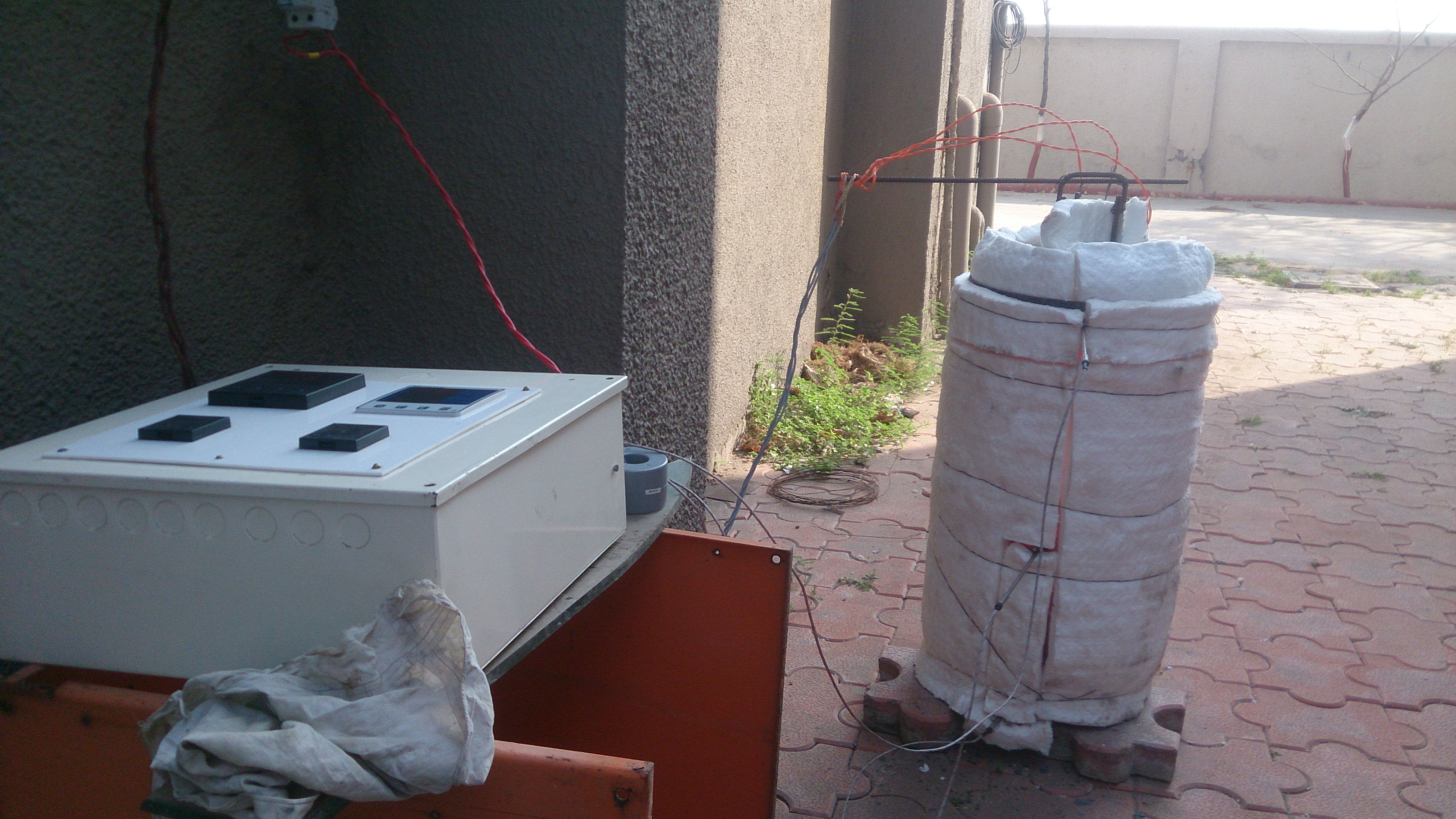
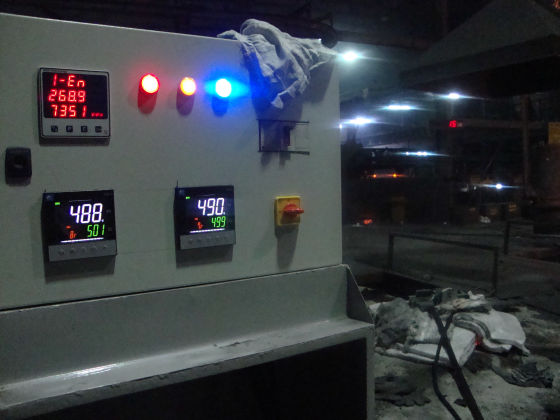
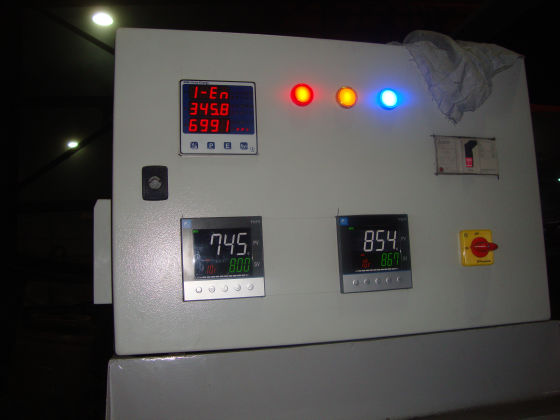
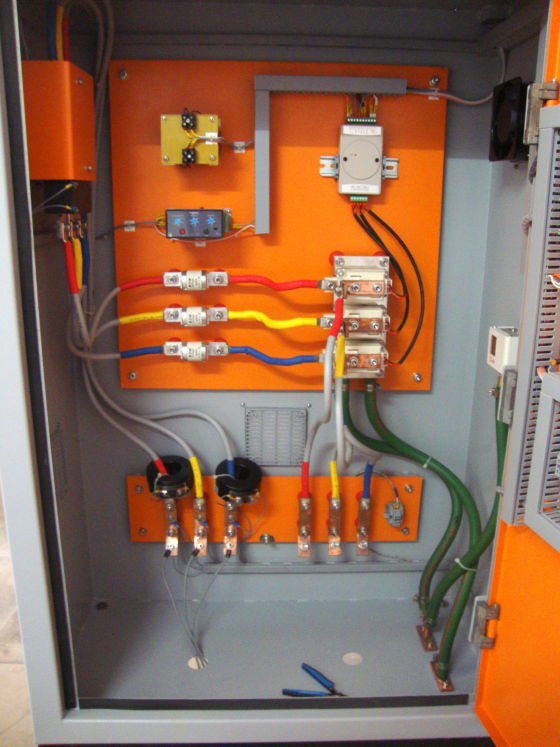
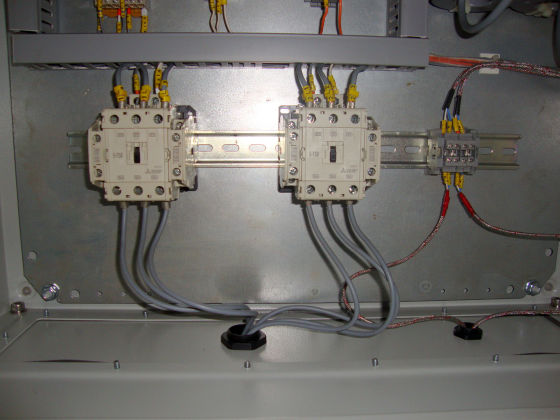
Each zone has its own set of thermocouples, profile controller and power circuit and can be controlled individually. This eliminates the need of labour for manually varying the power as well as for the charging of the scrap.
No Need of Auxiliary Equipment
More units saving is realised as auxiliary pumps are not required. Furnace cooling can be effectively done through over head tank or small water pump.
Safety is Priority
The Quick Sinter provides protection against short circuit fault along with earth leakage and open load detection. This ensures upmost safety of the personnel as well as of the equipment.
Optimum Plant Load Factor
As independent PSU is used, full power of the induction PSU can be utilized during sintering cycle, thus ensuring optimum utilization of the plant load.
Cold Starting of the Furnace
All the benefits of the Quick Sinter can further be realized when it is used during the Cold Starting of the Furnace.
Patching/Re-lining of the Furnace
Quick Sinter can be of further benefit by using it during the patching or re-lining of the furnace.